The Science Behind Dance, Play, and Child Learning
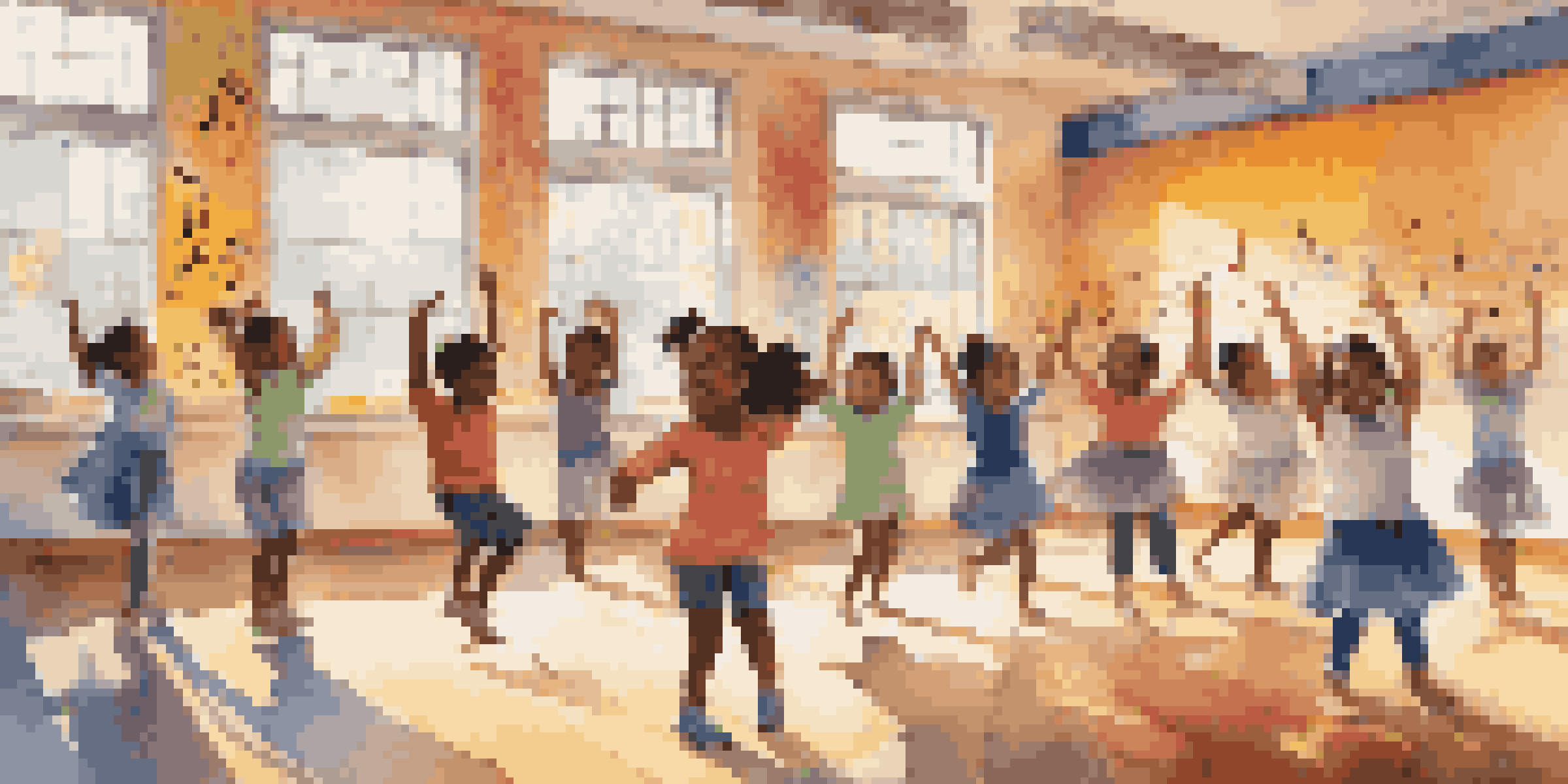

Understanding the Connection Between Movement and Learning
Movement is more than just a physical activity; it plays a crucial role in cognitive development. When children engage in activities like dance and play, they stimulate their brains, making learning more effective. This connection is rooted in the way our brains process information, linking physical activity to improved memory and problem-solving skills.
Play is the highest form of research.
For instance, consider how children often learn through songs and dance routines. These engaging methods not only make learning fun but also help reinforce memory retention through rhythm and repetition. When children move, they are not just exercising their bodies; they are also activating their minds in a dynamic way.
Research has shown that incorporating physical play into educational settings can significantly enhance a child’s ability to grasp complex concepts. This integration of movement with learning fosters a holistic approach, allowing children to absorb information more naturally and joyfully.
The Role of Dance in Cognitive Development
Dance is a unique form of expression that combines creativity, emotion, and physical movement. Engaging in dance requires children to remember sequences and patterns, which directly supports their cognitive growth. This process not only boosts their memory but also enhances their ability to focus and concentrate.
Moreover, dancing encourages children to think critically and make decisions on the fly, whether they're improvising or following a choreographed routine. This aspect of dance helps develop essential skills like teamwork and collaboration, as many dances are performed in groups, fostering social connections.
Movement Boosts Learning
Engaging in physical activities like dance and play enhances cognitive development and memory retention in children.
Additionally, research indicates that dance can improve spatial awareness and motor skills. As children learn to navigate their bodies in space, they become more aware of their surroundings, which can translate into better performance in other areas, including academics.
Play: The Foundation of Learning
Play is often touted as the 'work' of children, and for good reason. Through play, children explore their environment, test boundaries, and develop critical thinking skills. This unstructured time is vital for fostering creativity and imagination, which are essential components of learning.
Dance is the hidden language of the soul.
For example, when children engage in pretend play, they practice social roles and scenarios, helping them understand the world around them. This kind of imaginative play promotes empathy as they learn to see things from others' perspectives, a skill that is invaluable in both personal and academic settings.
Furthermore, play encourages resilience. When children face challenges during play, whether it's building a tower that keeps falling or navigating a tricky game, they learn to adapt and try again. This perseverance is a key trait that benefits them throughout their educational journey.
The Impact of Structured vs. Unstructured Play
While both structured and unstructured play are beneficial, they serve different purposes in child development. Structured play, such as organized sports or dance classes, provides children with opportunities to learn specific skills and follow guidelines. This type of play can enhance discipline and focus, essential traits for academic success.
On the other hand, unstructured play allows children the freedom to explore and create without limitations. This kind of play is crucial for fostering innovation and problem-solving skills. Children learn to navigate social interactions and develop their own rules, which helps them build confidence and independence.
Balance Structured and Unstructured Play
Combining structured activities with unstructured play fosters creativity, critical thinking, and social skills in children.
Balancing both types of play is key. A mix of structured and unstructured activities can provide children with the benefits of learning new skills while also allowing them the freedom to express themselves and explore their interests.
The Neuroscience of Dance and Play
Neuroscience has uncovered fascinating insights into how dance and play influence brain development. Engaging in these activities releases neurotransmitters like dopamine, which play a significant role in mood regulation and motivation. This not only makes children feel good but also enhances their capacity to learn.
Moreover, studies have shown that physical activity, including dance, increases the size of the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for memory and learning. As children engage in rhythmic movements, they are essentially giving their brains a workout that promotes healthy brain growth.
This scientific backing reinforces the idea that movement is essential for learning. When educators and parents recognize the importance of incorporating dance and play into daily routines, they can significantly enhance children's overall development.
Dance and Play as Emotional Outlets
Dance and play provide children with essential emotional outlets, helping them process their feelings. Engaging in these activities allows children to express joy, frustration, and creativity in a safe environment. This emotional expression is crucial for mental health and well-being.
For instance, dance can serve as a therapeutic tool, helping children to channel their emotions through movement. Whether it’s through a joyful dance or a calming routine, children learn to manage their feelings and develop emotional intelligence.
Dance and Play for Emotional Health
Both dance and play serve as vital emotional outlets, helping children process feelings and develop essential social skills.
Play, similarly, encourages children to work through social dynamics and conflicts, teaching them valuable lessons about empathy and cooperation. When children face challenges during play, they learn to negotiate, compromise, and resolve conflicts, skills that are vital for their future interactions.
Encouraging Dance and Play in Daily Life
Integrating dance and play into children’s daily routines can be both fun and beneficial. Parents and educators can create an environment that encourages movement by incorporating music and physical activities into everyday tasks. Simple actions, like having a dance party while cleaning, can make chores more enjoyable.
Additionally, setting aside time for unstructured play is critical. Allowing children to explore their interests without rigid schedules fosters creativity and independent thinking. Whether it’s playing outside, engaging in arts and crafts, or experimenting with dance, these moments are essential for learning.
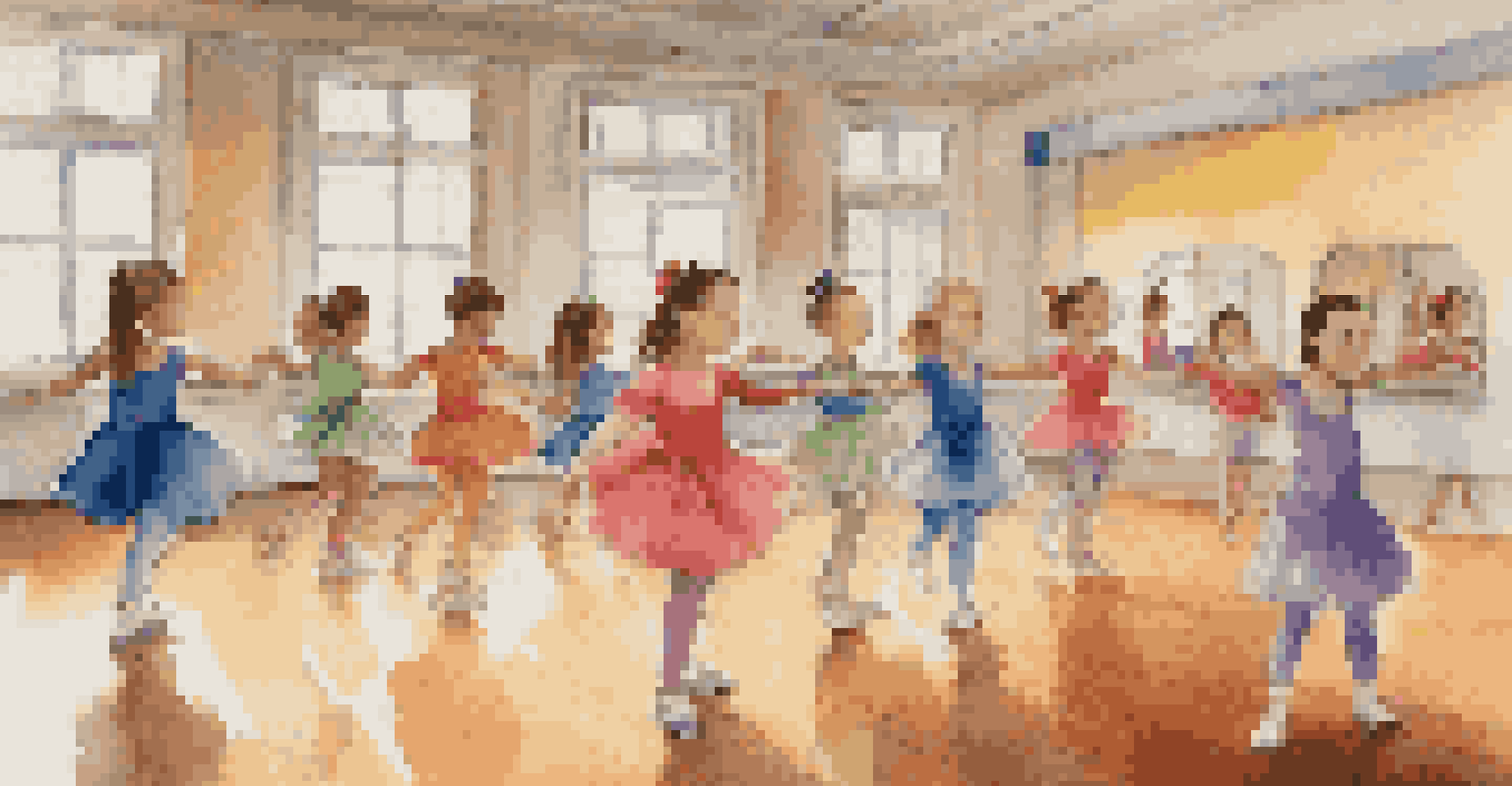

Lastly, community programs and classes can also provide structured opportunities for dance and play. By participating in local arts or sports initiatives, children are exposed to new experiences that can further enhance their learning and development.